Dirt Bike Engines
2 stroke vs 4 stroke bike engine
The four phases of combustion may be finished in a 2-stroke engine (Dirt Bike Engines) in just one whole crankshaft rotation. Two crankshaft revolutions are needed for a 4-stroke engine. This benefit explains why a 250 cc 2-stroke engine produces greater power than a 4-stroke of equal displacement.
Motorcycle engines, commonly referred to as dirt bike engines, are created specifically for off-road riding. Depending on the particular type of dirt bike and its intended purpose, these engines come in a variety of sizes, types, and configurations. Here are some essential characteristics of dirt bike engines.:
Engine Types:
Two-Stroke Engines:
2-stroke engines are renowned for being straightforward and light in construction. They create power every two piston strokes (up and down), have fewer moving components, and need less maintenance. Due to their excellent power-to-weight ratio, two-stroke engines are frequently employed in motocross and off-road racing.
Four-Stroke Engines:
Even though four-stroke engines are more complicated, they provide power more smoothly and use less gasoline. Every four piston strokes (up, down, up, down), they generate power. Dirt motorcycles used for enduro, trail, and dual-sport activities frequently use four-stroke engines.
Engine Displacement:
Different displacements of dirt bike engines are available; these are commonly expressed in cubic centimeters (cc) or cubic inches (ci). Dirt bike engines frequently have displacements of 50cc, 85cc, 125cc, 250cc, 450cc, and higher. The skill level, riding manner, and planned use of the rider all influence the engine displacement selection.
Engine Configuration:
Single, twin, or even multiple cylinder layouts are possible for dirt bike engines. Due to its simplicity, small weight, and adaptability for off-road use, single-cylinder engines are the most prevalent in dirt motorcycles.
Power Delivery:
2 stroke engines are preferred for motocross and racing because they frequently produce power more quickly and instantly. Four-stroke engines are better suited for lengthy journeys and difficult terrain since they provide power more smoothly.
Cooling:
Engines on dirt bikes can be either air or liquid cooled. To disperse heat, air-cooled engines rely on air circulation, whereas liquid-cooled engines utilize a coolant (typically a combination of water and antifreeze) and a radiator.
Fueling:
To provide gasoline to the engine, most current dirt motorcycles employ electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems. Carburetors may be used in older models. EFI provides improved fuel economy and performance management.
Maintenance:
For reliable operation, dirt bike engines need routine maintenance such as oil changes, air filter cleaning or replacement, valve adjustments (for four-stroke engines), and general inspections.
Performance Modifications:
To increase power and handling, riders often modify the performance of their dirt bike engines using aftermarket parts, exhaust systems, and engine mapping adjustments.
Electric Start:
Some dirt bike models include electric start systems, which make starting the engine easier, especially in difficult off-road settings.
Environmental Considerations:
Manufacturers have been creating cleaner and more ecologically friendly dirt bike engines in recent years, with an emphasis on lowering emissions and boosting fuel economy.
Which is better 2-stroke or 4-stroke motorcycle – Dirt Bike Engines?
The choice between a 2-stroke and a 4-stroke dirt bike engine depends on your riding style, preferences, and intended use. Each type of engine has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a comparison to help you decide which might be better for your needs:
2-Stroke Dirt Bike Engine:
Advantages:
Lightweight: 2-stroke engines are generally lighter than 4-stroke engines, which can lead to better handling and maneuverability.
Simplicity: They have fewer moving parts, making them easier to maintain and repair.
Strong Low-End Power: 2-strokes often have strong low-end torque, which can be advantageous for quick acceleration and jumps in motocross.
Lower Maintenance Costs: Due to their simpler design, maintenance costs can be lower.
Disadvantages:
Less Fuel Efficiency: 2-strokes tend to consume more fuel than 4-strokes.
Shorter Engine Life: They typically have a shorter engine lifespan due to higher RPMs and more frequent maintenance requirements.
Limited Emissions Compliance: Older 2-stroke engines may not meet modern emission standards in some areas.
Aggressive Power Delivery: The power delivery can be abrupt, which might be challenging for beginners.
4-Stroke Dirt Bike Engine:
Advantages:
Smooth Power Delivery: 4-strokes provide smoother and more predictable power, making them suitable for a wide range of riders, including beginners.
Fuel Efficiency: They are generally more fuel-efficient than 2-strokes.
Longer Engine Life: 4-strokes tend to have a longer lifespan with proper maintenance.
Emissions Compliance: Modern 4-stroke engines are more likely to meet emission standards in various regions.
Disadvantages:
Heavier: 4-stroke engines are typically heavier, which can affect handling, especially in motocross.
Complexity: They have more moving parts, which can lead to higher maintenance costs and more challenging repairs.
Less Low-End Torque: 4-strokes may have less low-end torque compared to 2-strokes, which can be a factor in certain off-road situations.
Ultimately, the “better” engine type depends on your riding goals. If you’re looking for simplicity, quick acceleration, and don’t mind more frequent maintenance, a 2-stroke might be suitable. On the other hand, if you value smooth power delivery, fuel efficiency, and longer engine life, a 4-stroke may be the better choice. It’s essential to consider your skill level, riding style, and the type of terrain you’ll be tackling when making your decision. Testing both types of bikes to see which one feels more comfortable and suits your preferences is often the best approach.
Which engine is more powerful 2-stroke or 4-stroke Dirt Bike Engines?

In general, 4-stroke engines of the same displacement are frequently seen as being less powerful than 2-stroke engines. But it’s important to realize that these two engine types’ power characteristics are very different from one another, and that an engine’s “power” can vary depending on how it’s measured and felt.
Here are some key points to consider:
2-stroke dirt bikes engine
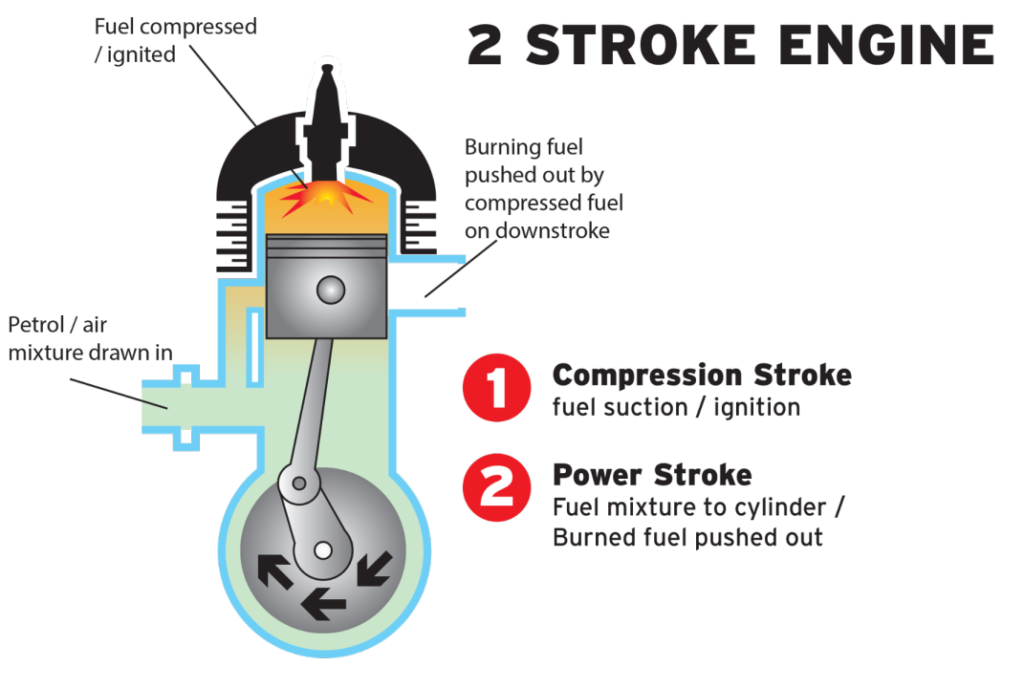
Two-stroke engines are able to provide excellent power-to-weight ratios because of their renowned low weight and straightforward design.
Every time the crankshaft turns, there is a power stroke (combustion), which increases the speed and responsiveness of the power supply.
Where rapid, high-revving power is required, like in motocross racing and some off-road riding, 2-stroke engines are frequently used.
4-stroke dirt bikes engine
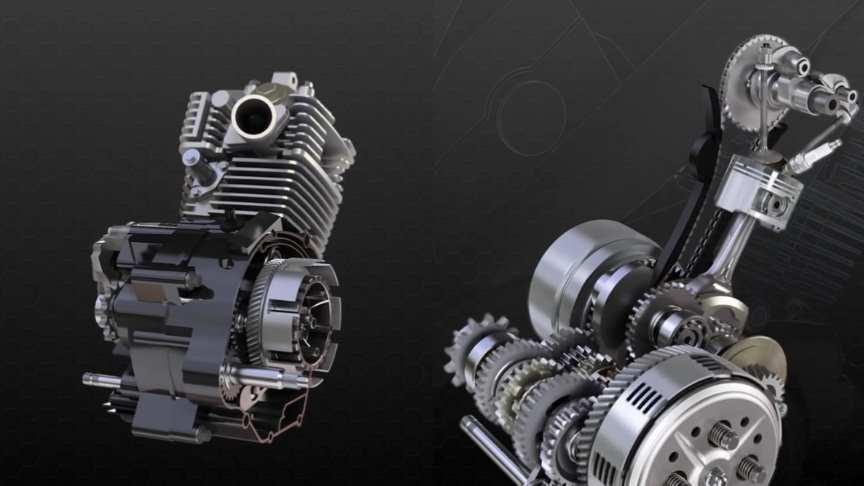

Because the intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes all occur within two crankshaft rotations, 4-stroke engine design is more difficult.
Because of their broader powerbands and smoother power delivery, they are suited for a wide range of riding styles and situations.
Torque is a property of four-stroke engines that may be useful for off-road and tough riding.
Power perception is also influenced by rider selection and riding technique. Some riders like a 2-stroke’s quick and strong burst of power, while others prefer a 4-stroke’s broader and more predictable powerband.
It is worth noting that advances in engine technology have blurred the distinctions between 2-stroke and 4-stroke power characteristics, and current 4-stroke engines are competitive in terms of power output and responsiveness, particularly in motocross and off-road racing.
Finally, the decision between a 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine should be based on your riding preferences, kind of riding, and ability level. Both types of engines have advantages and disadvantages, and they are best suited to certain applications.
FAQ about Dirt Bike Engines
What is the engine size of a typical dirt bike?
- A dirt bike’s engine size can vary greatly, although typical engine displacements for little children’s motorcycles range from 50cc to 450cc for large adults’ bikes. For some racing categories, there are also bigger displacements available.
2. What’s the difference between two-stroke and four-stroke dirt bike engines?
- Two-stroke engines are simpler in design and create power every two strokes of the piston, making them lighter and more responsive. Four-stroke engines are more sophisticated, producing power every four strokes and producing power that is smoother and more tractable.
3. How do I choose between a two-stroke and a four-stroke dirt bike?
- The decision is based on your riding style and preferences. Two-stroke engines are ideal for motocross and shorter races because to their lightweight and agility. Four-stroke engines have higher torque and are preferred for trail riding, enduro racing, and longer races.
4. What is the maintenance schedule for a dirt bike engine?
- Brand and model-specific maintenance regimens differ, but typical duties include routine oil changes, air filter cleaning and replacement, valve adjustments, chain upkeep, and general bike inspections. Regarding precise intervals, consult your owner’s handbook.
5. How often should I change the oil in my dirt bike engine?
- Oil types, riding conditions, and engine displacement all affect how often you should replace your oil. In general, oil changes may be required after a few rides or every 10–20 hours of riding, but for exact instructions, see your owner’s handbook.
6. What type of oil should I use for my dirt bike engine?
- The type of oil required is determined on the engine and use of your motorcycle. Many dirt motorcycles require certain types of motorcycle oil, and there are alternatives for both two-stroke and four-stroke engines. Always use oil that fits the manufacturer’s standards.
7. Can I modify my dirt bike engine for more power?
- Yes, it is feasible to boost the power of a dirt bike engine. Aftermarket exhaust systems, engine tuning, and performance upgrades are typical alterations. However, since incorrect changes might harm the engine, exercise caution and seek advice from professionals.
8. How do I break in a new dirt bike engine?
- Over the course of the first several hours of riding, a fresh dirt bike engine’s RPM and load are steadily increased. This ensures longevity and performance and enables the engine parts to break in correctly.
9. What is the top speed of a typical dirt bike?
- Top speeds vary based on the engine capacity and gearing of the motorcycle. Smaller dirt motorcycles can achieve speeds of 40-50 mph, whilst larger and more powerful ones may reach speeds of 70 mph or more.
10. How do I diagnose and troubleshoot engine problems in my dirt bike?
– Checking for signs like strange noises, poor performance, or smoke is one step in the diagnosis of engine problems. Carburetor troubles, clogged spark plugs, or worn engine parts are examples of common issues. For correct diagnosis and repair, consult a skilled technician.
11. Can I rebuild my dirt bike engine myself?
– A dirt bike engine rebuild is a difficult undertaking that needs mechanical know-how and specific equipment. The easiest way to guarantee good installation and function is frequently to leave it to skilled experts or knowledgeable technicians.
Conclusion:
Please be aware that dirt bike engines can vary significantly depending on brand, model, and year, so it’s critical to refer to the owner’s handbook for your particular dirt bike and adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions for maintenance and care.





